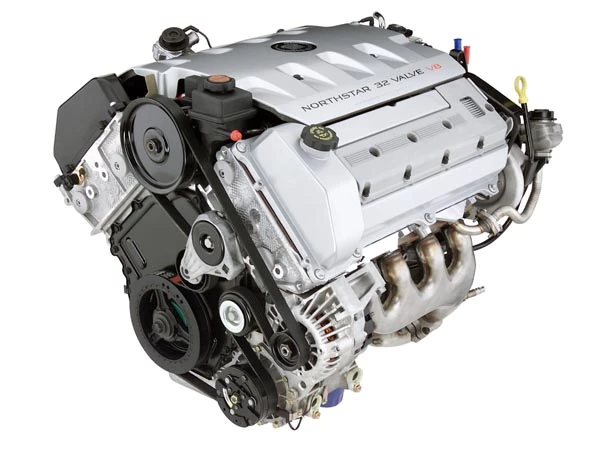
It is believed that the Northstar engine was built between 1993 to the year 2011. It is a common 90-degree Double overhead cam V8 that has four valves for each cylinder. It is believed to be a technically advanced engine.
Despite its success, however, the engine was plagued by common engine problems that negatively affected the reliability of Northstar engines.
In today’s post today’s article, we’d like to give you a checklist of the best year for Northstar engines to steer clear of. Stay tuned and continue reading!
What Year Northstar Engines To Avoid?
What Year Northstar Engines To Avoid?: 1993 – 1999 Northstar L37, 1994- 2002 Northstar LH8, 2004 – 2005 Northstar LH2, and 2006- 2009 Northstar LH2 and LC3. Below are their most common issues.
1993 -1999 Northstar L37
Northstar L37 engines built before 2000 cannot insert the rear washers into the block.
Thus, the 1993 Northstar engine issues resulted from crankshaft rotation turns while the sealing wore rapidly.
The primary seal on the rear prevents oil leakage at the crankshaft’s exit. If it’s broken, oil could leak.
1994 – 2002 Northstar LD8
The Northstar LD8 engine is believed to have issues due to lubrication in the vehicle. The cause is a substance stuck inside the tension relief valve.
More recently, 1999 Northstar engine issues were characterized by leaks in valve plates. The early Northstar LD8 engine models are more vulnerable to sudden drops in the fuel pump.
It isn’t easy to repair the pads. The proprietor will have to spend significant time replacing seals and gaskets to fix the problem.
Take the fuel pump off and wash the dirt If you notice a decrease in the pressure relief valve for oil.
In addition, one of the 2001 Northstar engine issues was that it used a lot of oil.
The problem is that rings can become trapped when there is an accumulation of carbon within the rings. Rings that are stuck in slots will not be able to lubricate either the motor or crankcase.
Performance efficiency and fuel consumption could be reduced significantly due to this.
2004 – 2005 Northstar LH2
Head washers failing to function correctly are standard in 2003 Northstar engine issues.
Due to design imperfections, the LH2 Northstar engine was in danger of overheating. When an engine uses excessive oil, carbon builds up.
The carbon buildup causes an increase in the temperature of the engine. As a result, the head gasket may be blown out.
The TTY bolts are fastened to the motor’s head. Once they become tight, the bolts begin stretching.
Once the yield bolts have been loose, the head strays away from the block as the bolt head gets squeezed.
The bolts have to be reset following removal, and that’s why the gasket in the head could be blown away. We’ll explain the issue in detail below.
2006 – 2009 Northstar LC3
One of the most common problems with Northstar LC3 engines is warming the glow plugs. The glow plugs are vulnerable to melting and causing severe damage and may also break.
The excessive rotation of plugs caused by the glow component is at the root of the problem. Several owners brought this issue up on the forum.
In addition, oil leakage via the confirmed lubricating pipe is a problem in the Northstar LC3. Most of the filters in the crankcase of the LC3 engine can be prone to oil spillage.
The turbine’s rotors are coated with oil and accumulated within the compressor. This hose with the silicone glue that is at the bottom also gets eaten. It makes a hole as a result and then explodes.
What Is The Worst Year Northstar Engines?
The Northstar L37 is GM’s weakest Northstar engine demonstration.
As previously mentioned, older vehicles with L37 Northstar engines could have leaky gaskets and cylinders. Northstar engines built in 1993 and 1994 had blocked push-button oil valves.
This was a severe problem because drivers had to replace gaskets and the seals.
What Are Northstar Engines Problems?
Are Northstar engines bad? Despite being used for over 18 years, Northstar engines still suffer from various problems.
Motor design is primarily to blame for the majority of these issues. Although some problems have been resolved, other issues remain frequent, even on newer Northstar models.
Blower Head Washer
All Northstar engines are prone to head seals that fail. TTY bolts, also known as tension transmission bolts, are installed on the head of the rotor.
Since these bolts are not permanent, when you remove them, they have to be replaced.
The process of stretching takes place when the TTY bolts tighten. The screws expand more as the cylinder heats, and unlike many other products, they do not shrink following freezing.
The head slides onto the cylinder while the bolts are stretched, causing the carburetor to explode.
While it is true that the Northstar engine is designed to resist overheating, design flaws can lead to this happening.
They use plenty of oil. This results in a massive carbon build that we will explore more in-depth.
This buildup of carbon causes an increase in engine performance and could lead to a gasket blowout.
In addition, the head gasket could also suffer damage if the bolt is removed and reused instead of replaced.
Rear Main Seal Oil Leak
The seal at the rear of Northstar engines built after 1999 often leaks oil.
The block’s bottom, where the crankshaft exits, will be the primary seal at the rear. It’s responsible for preventing oil leaks from an outlet on the crankshaft.
Before the 2000 engines, Northstar did not use press seals, even though most of the seals on the rear were placed in the engine block. This means that the seals deteriorated faster when the crankshaft rotated.
Furthermore, low brake fluid levels can cause seals to deteriorate and leak more frequently, which requires flushing- and frequent oil changes.
In the end, if a vehicle is not used for long periods in a row, the seals can be damaged and dry and leak, leading to leaks.
Valve Cap Oil Leak
When lubricating camshafts or valves, an oil leak is prevented through the cover of the valve on top of the cylinder head.
A gasket between the cover and the top of the head seals the valve cover similarly to how it fills the cylinder head.
The valve caps cracking or insufficient valve seals could result from Northstar overheating. A defective valve cover gasket can also cause leaks in the vacuum.
Tiny pores in the valve cap are often caused by damage to the cap. As the fissures grow, they are pushed to push oil out of them. When they produce more, leaks occur.
Gaskets can fail due to wear and tear. As they age, the chance of them falling is higher.
Excessive Oil Consumption
Leaks can trigger an increase in oil consumption. However, in this situation, this is because the combustion chamber is burning oil. As mentioned earlier, carbon deposits will likely build up within the grooves of piston rings.
When this happens, the rings are encased by the ring’s surface, and dirt can’t be removed from the cylinder’s wall. The oil is ignited inside the cylinder walls because gas is forced through the crankcase.
Carbon Accumulation
The buildup of carbon and its role in various joint problems, such as broken head gaskets and poor performance, has long been debated in detail.
Not only engines before 2000 were faced with the carbon buildup caused by piston rings. Engines running from 2000 through 2002 also faced this issue.
Carbon builds up frequently within the cylinders of these cars.
The ignition process heats the combustion chambers. Heat is generated within the cylinders, igniting oil, which causes engine blocks to rattle or shake as the car accelerates.
What Year Northstar Engines Are Good?
Remember that they are Northstar engines, which are worth buying.
- The Northstar L47 engine gained notoriety at the racetrack. A 650-horsepower version of the L47 Northstar joined the 1995 championship of sports cars.
The L47 is a twin-turbo model used in a twin-turbo model for the Cadillac Northstar LMP program. It typically produces 290 pounds of torque and 320 horsepower.
- The V6 L47 Aurora motor drives the LX5 “Shortstar.” The crankshaft of the Northstar keeps the 90° V-angle. This Northstar LX5 produces 234 pound-feet with the ability to traction and 215 horsepower. Its predecessor, the Short Star, was discontinued in 2004.
Are Northstar Engines Reliable?
The correct answer is yes and no. The engine’s technological advancements have resulted in a few minor problems.
While most issues we’ve discussed seem easy to fix, they’re not. Simple repairs are costly and time-consuming due to engine design.
The expense of maintenance and troubleshooting is the Northstar’s reliability problem.
Northstar is one of many significant engines to have. However, despite a few imperfections in manufacturing, it’s not a total disaster due to its power and lower noise.
Conclusion
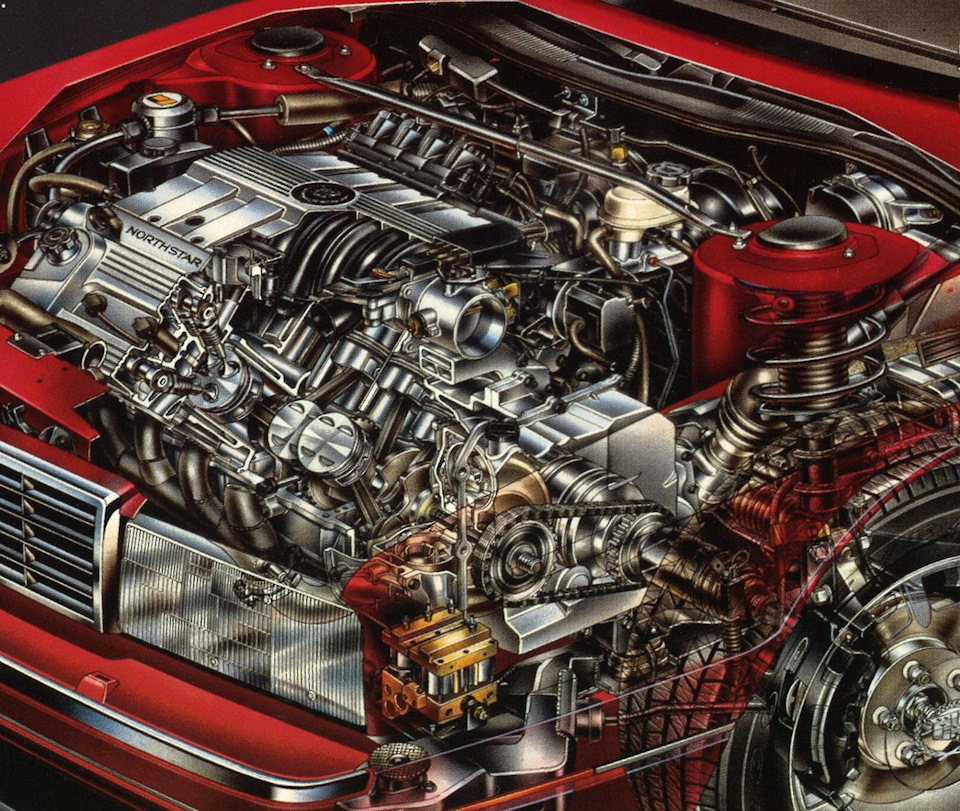
image source:drive2.ru
To summarize, the years Northstar engines to steer clear of comprise 1993-1999 engines, 1994 to 2002 Northstar LD8, 2004- 2005 Northstar LH2, and 2006 – 2009. Northstar LC3
In addition, the article will help you recognize some common issues with Northstar engines.
Oil leaks, head gasket failures, and carbon b buildup, to name several issues in the case, are possible with aging.
Related topic: G-wagon years to avoid










